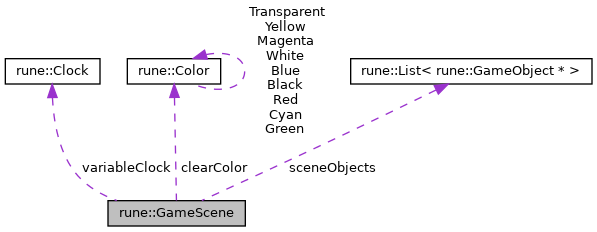
This class is responsible for serving as a parent class for each instance of the game. In order to create a new instance for the game, copy this class and add objects as needed.
More...
#include <gameScene.h>
This class is responsible for serving as a parent class for each instance of the game. In order to create a new instance for the game, copy this class and add objects as needed.
- Author
- Thomas Montano
- Date
- March 2 2020
◆ deInit()
| void rune::GameScene::deInit |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
DeInit is responsible for marking this state to be cleaned up
◆ doInit()
| void rune::GameScene::doInit |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
Initializes the state.
DoInit is responsible for initializing this State. HandleCleanup will be called if mCleanup is true so Derived classes should always call IState::DoInit() first before initializing their assets.
◆ Draw()
Draw is responsible for handling all Drawing needs for this State when it is the Active State.
- Parameters
-
◆ handleCleanup()
| void rune::GameScene::handleCleanup |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
HandleCleanup is responsible for performing any cleanup required before this State is removed.
◆ handleUI()
Handle scene level UI that needs to be run independent of the update rate.
- Parameters
-
| window | Render window that should be used for mouse positions |
◆ isActive()
| bool rune::GameScene::isActive |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
Determines whether or not the scene is currently active.
- Returns
- Whether or not the current scene is flagged as active.
◆ pause()
| void rune::GameScene::pause |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
Pause is responsible for pausing this State since the Application may have lost focus or another State has become activate.
◆ reInit()
| void rune::GameScene::reInit |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
Reset the scene without unloading game objects.
ReInit is responsible for Resetting this state when the StateManager::ResetActiveState() method is called. This way a Game State can be restarted without unloading and reloading the game assets
◆ renderScene()
Makes all of the draw calls for the scene.
- Parameters
-
- Warning
- This function is only meant to be used in between a frame buffer bind and unbind only.
◆ resume()
| void rune::GameScene::resume |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
Resume is responsible for resuming this State since the Application may have gained focus or the previous State was removed.
◆ submitToRenderer()
| void rune::GameScene::submitToRenderer |
( |
rune::Drawable & |
newDrawable | ) |
|
Submits a drawable object into the rendering stack to be drawn to the screen each frame.
- Parameters
-
| newDrawable | a pointer to an object that needs to be drawn to the screen. |
◆ updateFixed()
| void rune::GameScene::updateFixed |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
UpdateFixed is responsible for handling all State fixed update needs for this State when it is the active State.
◆ updatePhysics()
| void rune::GameScene::updatePhysics |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
Update the RigidBodies in the scene.
◆ updateVariable()
| void rune::GameScene::updateVariable |
( |
void |
| ) |
|
|
virtual |
UpdateVariable is responsible for handling all State variable update needs for this State when it is the active State.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: